🧠 Introduction
Dreams can be strange, beautiful, or terrifying — but why do we dream at all?
For centuries, dreams were seen as messages from the gods or the unconscious mind. But today, neuroscience offers real clues into what dreams are, why they happen, and how they affect your memory, mood, and even creativity.
Let’s dive into the science of dreaming.
🛏️ What Happens When You Sleep?
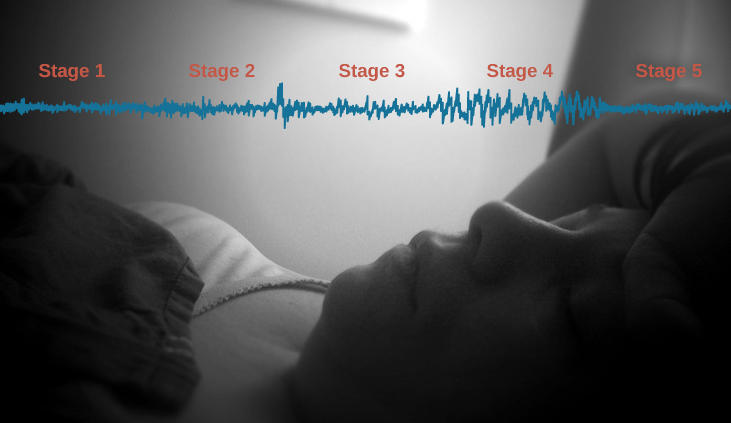
Sleep isn’t just “switching off.” Your brain goes through 5 stages of sleep, including:
- Stage 1 & 2 – Light sleep
- Stage 3 & 4 – Deep (slow wave) sleep
- Stage 5 – REM sleep (Rapid Eye Movement)
REM sleep is when most vivid dreaming happens. Your brain becomes active, heart rate increases, and eyes move quickly behind your eyelids — but your body stays still.
🌌 Why Do We Dream? 4 Scientific Theories
1. 🧹 Memory Processing
Dreams help sort and store your memories.
Studies show the brain replays parts of your day during sleep, organizing them into long-term memory.
Dreaming may be the brain’s way of cleaning its hard drive.
2. 🛡️ Emotional Regulation
Ever woken up less anxious after a bad day?
Dreams may help process emotions, especially negative ones. They allow your brain to simulate scenarios, work through stress, and improve emotional balance.
3. 🧪 Problem Solving & Creativity
Some inventors and artists got their best ideas from dreams.
Dreams can mix ideas in weird, abstract ways — triggering creative breakthroughs or new solutions to real-life problems.
🧠 Fun Fact: Paul McCartney said the melody for “Yesterday” came to him in a dream.
4. 🎭 Simulation Theory
Dreams may simulate “practice runs” for life.
They create imaginary situations (chases, arguments, accidents) so your brain can prepare for threats or social interactions.
🔍 What Influences Our Dreams?
- Stress or anxiety – Can lead to intense or negative dreams
- Foods – Spicy meals before bed can increase vivid dreams
- Medications – Some affect REM sleep cycles
- Sleep quality – Poor sleep = less REM = fewer dreams
- Lucid dreaming – When you become aware you’re dreaming and may control it
🌈 What About Dream Meanings?
Are dreams symbolic?
Psychologists like Freud believed dreams are full of hidden meanings — like desires or fears from the subconscious.
Modern science leans toward:
Dreams reflect your thoughts, memories, and emotions, not universal symbols.
That scary elevator dream? Might just be your brain’s creative remix of stress, movies, and muscle memory.
🧪 Can We Study Dreams in Labs?
Yes! Neuroscientists use EEG and MRI scans to study brain waves during sleep.
They’ve even trained AI models to predict visual content from dream-related brain activity.
We’re still far from recording dreams like movies — but science is getting closer to decoding them.
💤 Final Thoughts
We may never fully understand dreams — but we do know this:
They help your brain process, protect, and create while you rest.
So the next time you dream something wild or confusing, remember: your brain’s just doing maintenance, art, and therapy — all while you sleep.
📬 Call to Action
Do you remember your dreams?
Share your weirdest one in the comments and don’t forget to subscribe to MindFactual for more science-powered curiosity content.



